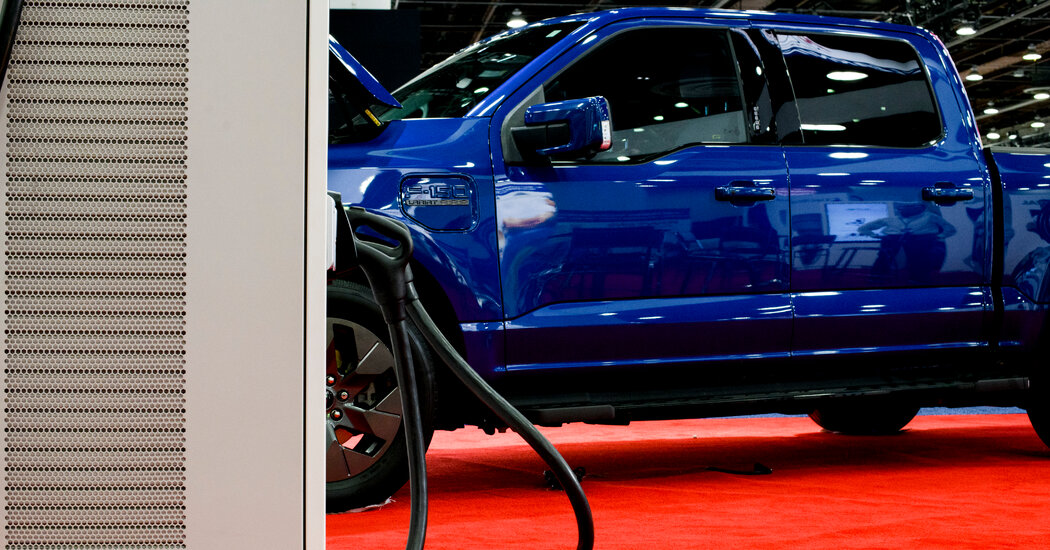
Ford Motor announced on Tuesday that it is recommencing construction of its electric vehicle battery facility in Michigan, albeit with scaled-down ambitions, attributing the change to the sluggish uptake of electric vehicles (EVs) in the US.
The revised plans for the Marshall, Michigan plant now anticipate the creation of 1,700 jobs, a reduction from the initially projected 2,500. Despite this, Ford maintains its target to commence production by 2026.
“The growth in demand for electric vehicles hasn’t met our initial expectations,” stated Ford’s spokesperson, T.R. Reid. Recent quarters have seen a rise in EV sales among major automakers like Ford, but not at a pace aligned with the aggressive targets set by the Biden administration.
- Kangana Ranaut Extols Shah Rukh Khan’s Superhero Journey, Calls Him India’s ‘Cinema God
- Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum: A Life of Leadership and Vision
- NEURC Launches Investigation into Alleged Illegal Actions by DTEK Akhmetov
- Ukrainian Forces Penetrate Russian Defenses, Escalating Southern Counteroffensive
Originally, the facility was designed to produce batteries with a total capacity of 35 gigawatt-hours per year, estimated to supply around 400,000 vehicles. However, the output has now been curtailed to 20 gigawatt-hours annually, sufficient for approximately 230,000 vehicles, marking a 42.8 percent reduction.
Ford has not disclosed the exact figure by which it will reduce its investment in the project but indicated that it would correspond to the lowered production capacity. Applying the 42.8 percent reduction to the initial investment of $3.5 billion suggests a cutback of about $1.5 billion.
The suspension of construction in September was attributed to concerns over competitive pricing in manufacturing. This decision came amidst intense negotiations with the United Automobile Workers (UAW) union.
Ford also cited escalating labor costs as a reason for downsizing the project. The recent contract agreement with the UAW, ratified by union members, includes a 25 percent wage increase for top-tier production workers.
This agreement facilitates the transfer of UAW members to new battery and EV facilities, like the Marshall plant. Workers at these sites will be covered by the UAW contract should they opt for unionization.
The UAW is striving to maintain its membership levels during the EV transition, facing resistance from automakers who argue that unionization places them at a competitive disadvantage against non-union rivals.
The UAW had not commented on the matter as of Tuesday.
Ford has also been scrutinized by conservative politicians for its plans to license technology from CATL, a Chinese battery manufacturer. The US currently does not produce lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries, a type imported by some American EV makers, including Tesla, from China.
The eligibility of US companies using foreign-licensed technology for government incentives aimed at transitioning from fossil fuels remains uncertain. However, Reid expressed confidence in Ford’s technology licensing agreement for the Marshall plant.
More News:
- Hayek celebrates his birthday in Greece
- If you want investment – create conditions
- According to the law, from September 1, the minimum wage will rise to UAH 5,000.
- Attempts to interfere with Sytnik are not new, even during the period of Zelensky’s state leadership.
- A big jump in the Central Bank of Gold balance